Definition and meaning of Faceted Navigation
Category/archive pages of websites that deal with many listings use faceted navigation (also known as faceted search) as a means of locating your way around. Users can use multiple filters based on the listing’s faceted navigation attributes to find what they’re looking for more quickly.
An Ecommerce website’s “faceted navigation” lets users filter and sort results according to product faceted navigation attributes.
Using Adidas.co.in faceted navigation examples, users can quickly narrow their search results by selecting criteria like the type of shoe they want, color, and size.
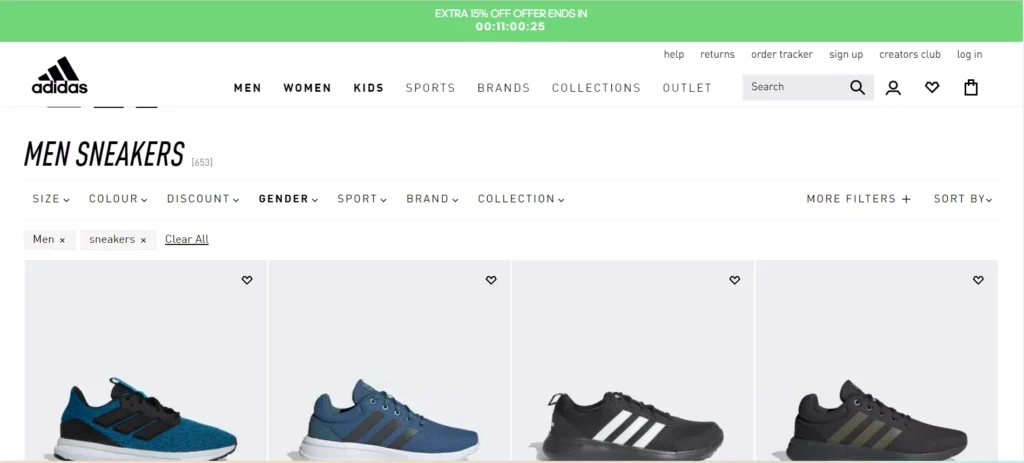
Optionally, the URL can be updated to reflect the selections made after applying the filters. The URL’s nature at this point can also vary:
- It has no effect. Without modifying the URL, the listings are updated.
- URL parameters such as https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers?v_size_en_in=9 are appended to the URL.
- A hash, such as #color=blue, is appended to the URL by the site to identify the facets applied.
- New URLs like /men-sneakers/blue/ (the user is using the “blue” facet in this example) are created for the user.
In what ways could faceted navigation harm your SEO efforts?
Observe how the URL changes depending on which option you choose. This is important for search engine optimization. Assuming you do the math, you could end up with millions of URLs that don’t add much value to searchers, which can be an SEO nightmare:
- A simple filter change will keep all page elements identical even if these URLs create duplicate content.
- Index bloat.
- These URLs can eat the crawl budget, particularly on large Ecommerce sites.
URLs create duplicate content
An example of duplicate content is if the same or similar content can be found at multiple locations on the website. Filters generate many URLs with the same content. This is mainly due to filter pages being nearly identical to the original page with only minor differences in their content.
Now checking the E-commerce website, Addidas.co.in.
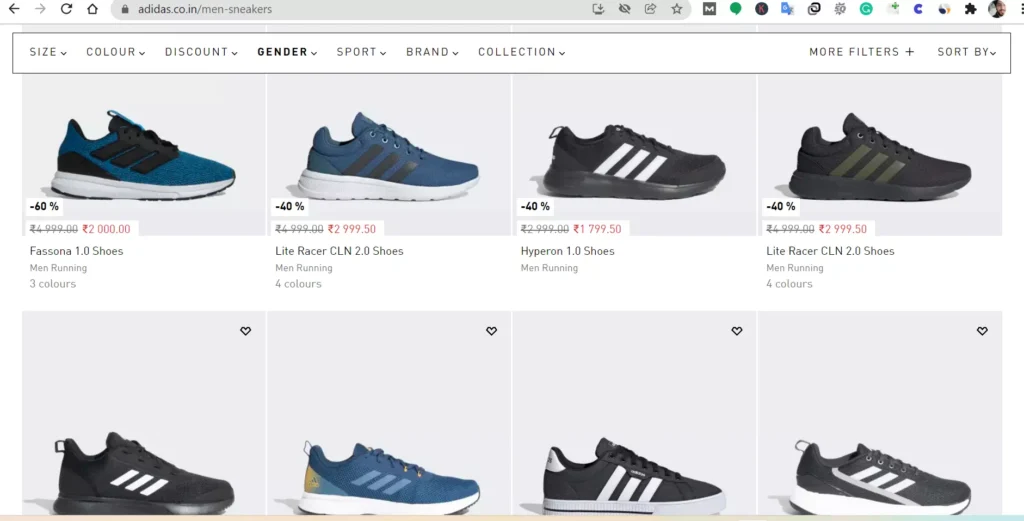
You can see the URL of the product listing – https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers
Now apply the filter for “Size-9“
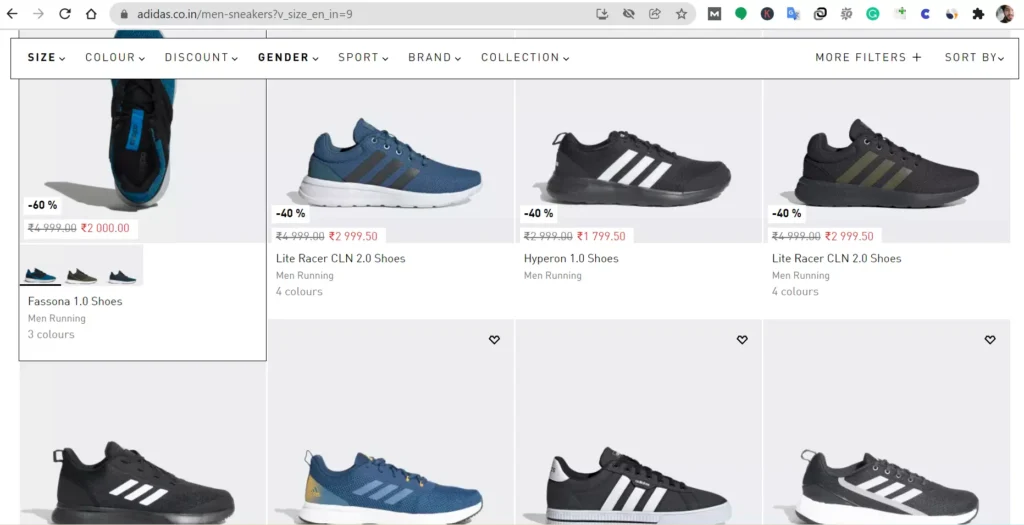
Now, the URL of the product listing change to – https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers?v_size_en_in=9
URL go from:
https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers
To:
https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers?v_size_en_in=9
This same block of content can also be found at the bottom of the page when scrolling right back.
Every filter can be used to create millions of duplicate pages for Google to consolidate into a single canonical page.
Also Check- Ways to Improve Website’s User Experience (UX)
Index bloat
Search engines can potentially index millions of URLs with no unique content because of faceted navigation meaning.
Using filters, a user visited the page can easily decide what they are looking for. The webpage returned exactly the same result what the user’s need.
These filters generate different URL’s which lead in creating index pages that don’t have a search value and might affect negatively in faceted navigation algorithm.
Crawl budget can be eaten up by these URLs
What is Crawl Budget?
On any given day, Google will crawl a fixed number of pages on your site, known as your crawl budget. This number keeps changing a little bit from day to day, but it is generally constant.
Wastage of Crawl Budget
If you don’t mind index bloat, this also means that you’ll be sending Google millions of URLs to crawl, which means that crawl budget management will be a necessity. Every possible combination of filter cause in a crawl budget, which immediately create an issue for search engine for crawling a website.
How can you tell if your faceted navigation approach isn’t working properly?
See if pages are indexed by search engines
Faceted Navigation examples, it gives you an idea of the scope of the issue. URLs may not be indexed, so the issue is completely irrelevant.
Have a look on your Robots.txt file
You can check if these subfolders have been blocked from crawling by visiting your Robots.txt file (or by robots.txt tester).
Site Crawl with Site Auditors Tool
It is possible to rectify the issue with the help of site auditing tools like SEMrush’s Site Audit or Screaming Frog.
There are many URLs to deal with, and the “Canonical link element” may be used to determine whether or not this issue can be corrected by canonical.
Ways to fix faceted navigation issues/faceted navigation best practices
Using Canonical tag
Setting canonical tag is one of the best solutions, if your website is not huge.
A facet page canonicalizes to the non-facet page, but those link signals aren’t lost; search engines pass them on to the category page, which may help it rank better in search results.
For example:
Facet Page: https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers?v_size_en_in=9
Canonical: https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers
Adding canonical tag, which would look like:
<link rel=”canonical” href=” https://www.adidas.co.in/men-sneakers”/>Configuring URL Parameters report in GSC
The URL parameters report in GSC is probably the best way to optimise crawling if canonicalization did not fix the indexing issues. It allows you to instruct Google on how to better crawl your URLs based on the parameters you specify.
Because URL parameters are required for the URL-based navigation, this method can only be used with URL parameters.
The URL parameters report is simple to use. Simple, just add a parameter and tell Google how it impacts the content of the page and whether or not it should crawl any exceptions.
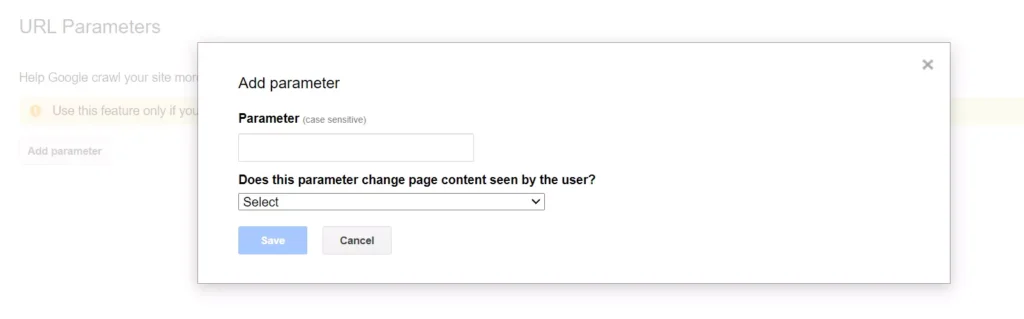
Note: Just make sure you understand how parameters work before using this feature. Google may remove many pages from search results if you incorrectly exclude URLs.
More details can be found by following Google’s instructions on how to use URL Parameters in Webmaster Tools.
Fixing crawl via robots.txt
The best of the three, but it may not be possible depending on how your URLs are generated. Although this is simple to implement in your robots.txt file, the link equity will be trapped in these pages. Understanding how your site’s links are distributed is critical if you want to use this strategy.
Add disallow rule in robots.txt for block crawling of URL:
User-agent: *
Disallow: * v_size_en_in=*
Nofollow or remove internal links on faceted navigation
The robots.txt is a directive, but Google now treats the rel=’nofollow’ attribute as a hint.
While an external nofollow tells Google that the href attribute is important, an internal nofollow tells Google to ignore the href attribute.
John Mueller, Search Advocate Google said:
“It’s not 100% defined but the plan is to make it so that you don’t have to make any changes, so that we will continue to use these internal nofollow links as a sign that you’re telling us:
- These pages are not as interesting
- Google doesn’t need to crawl them
- They don’t need to be used for ranking, for indexing.”
NOINDEX tag to fix indexing
Each of these pages can use NOINDEX tags, but doing so has a number of drawbacks:
- It is possible that search engines are still crawling pages with NOINDEX tags, wasting crawl budgets on millions of pointless pages.
- Because they aren’t indexed, these pages are gaining link equity at the expense of other pages that are.
To implement Noindex tag, add this code in the <head> of the faceted URL:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">Also Check – How to Embed Twitter Feeds on your Shopify Store
Conclusion
Hopefully, you’ve gained a better understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of using faceted navigation approach for SEO and long-tail search. Before launching your website, weigh the benefits and drawbacks carefully. To be honest, I’d love to tell you which is best, but I can’t because it all comes down to your website.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Faceted Navigation
Product attributes can be filtered and sorted using faceted navigation. Using an insightful user interface, faceted navigation makes it easier for customers to find information on a website.
How Faceted navigation works
You can quickly find what you’re looking for thanks to faceted navigation, which provides context to your search. As a whole, the facets provide a multi-dimensional view of searchable content and can identify inter-content relationships.
What is faceted navigation
To make it easier for customers to find the specific item they’re looking for, websites use faceted navigation.

